Lexicon of professional photographers

For ease of perception of information, all terms are collected in alphabetical order. Let's start, as usual, with the letter A.
Aperture is a concept identical to the diaphragm. In short, this is a mechanical hole in the lens that regulates the flow of light on the way to the camera's matrix. The smaller the aperture value, the more light the lens lets through, and vice versa.
Artifacts are visible defects in a photograph that occur due to the loss of information about a part of the frame. The impetus for the manifestation of artifacts in a photograph can be incorrectly selected settings or, for example, data loss during image compression.
Bayonet — a device for attaching optics to the camera body.
Shoe — an accessory port with a sync contact on the upper end of the camera for connecting all kinds of peripherals in the manner of an external microphone, on- camera light, radio synchronizer. Most often used together with the prefix "hot" ( hot shoe).
WB is shorthand for white balance.
Mirrorless is a camera with interchangeable lenses without a bulky mirror mechanism in the design.
Pancake is a thin and compact lens, often with a fixed focal length. The nickname is due solely to the miniature thickness of the pancake lenses.
Body — a complete set of a camera without a lens.
Bokeh is the characteristic blurring of a part of an image that is out of focus. In many cases, the background is deliberately blurred by the photographer in order to visually emphasize the main subject of the shooting. Particularly colorful bokeh is “drawn” by portrait optics with a large aperture.
 |
| The nature of the “pattern” of bokeh directly depends on the number and shape of the aperture blades of the lens. |
Barrel — geometric distortion when shooting at a wide angle, manifesting itself in the form of swollen lines closer to the edges of the frame.
Bracketing (fork) is a shooting technique during which several frames are taken with different exposure settings. It is used for subsequent merging of images into a single HDR image. Also, the use of bracketing allows you not to “screw up” the frame due to an unsuccessful selection of shooting settings.
Back focus is a phenomenon when the area of sharpness in a photo shifts forward in relation to the subject due to an incorrectly adjusted focus system. It is found purely on board SLR cameras.
Sighting — observation of the target (object of shooting) through the "peephole" of the viewfinder or the camera screen for a better frame composition.
A business card is a piece of paper that directs the light of an external flash. It often resembles an ordinary business card in shape.
Gradient is a slang term for a gradient filter.
DOF — depth of field. This is a visible line within which objects are displayed in the image with sufficient sharpness.
DD is an abbreviation for the dynamic range of photography.
The long end is the maximum focal length of the zoom lens. For example, for the Sigma 18-35mm f/1.8 DC HSM Art model, its value is 35mm.
A hole is a slang term for a lens aperture hole.
A lighter is a device for controlling studio lighting. Mounted on the hot shoe of the camera.
Hare — glare when shooting with back or side lighting. Especially often "hares" can be seen in photographs on bright sunny days. Anti-reflective lens coatings and lens hoods come to the rescue in the fight against "bunnies".
 |
| In addition to protecting against glare, the lens hood protects the front lens of the lens from mechanical damage and even from curious animals (as in the photo above). |
SLR — "folk" name for SLR cameras.
Zoom is a zoom lens.
Pencil is a cleaning agent for removing grease from the surface of the front and rear lenses of interchangeable optics.
The kit is the lens that comes with the camera.
A compact (digital compact) is a small camera with non-replaceable lenses.
The short end is the minimum focal length of the zoom lens.
Crop — cameras with a reduced matrix (in relation to full-frame models) have the stigma of "cropped". Also, this term is used when it comes to cropping (cropping) an image.
Canonists are adherents of Canon photographic equipment.
The lens is the same as the lens.
Burdock is a large-diameter diffuser for studio flash.
Makrushnik — there are two main meanings of this term:
- makrushniks are called followers of the genre of macro photography;
- ...and macro lenses.
 |
| Macro photography is a separate multifaceted world of photography. |
Manual — a synonym for the word "manual". It implies manual setting of parameters of pulsed light, focus (manual focus), etc.
Soap is a blurry shot without clear focus. Also, "soapy" refers to photos of deliberately low quality.
Soap dish (digital soap dish) is a compact camera with non-replaceable lenses and modest photo capabilities.
The leg is one of the support points of a tripod or a monopod.
Nikonists are supporters of photographic equipment under the sign of the Japanese company Nikon.
Dandelion is an adapter for non-autofocus optics of the old school, which allows you to catch the moment of focus and confirms focus in the viewfinder.
Screwdriver — a motor drive in the camera body for controlling the operation of autofocus lenses without its own motor. He got his name because of the resemblance to a screwdriver bit.
Oversharp — excessive sharpness of the image.
Pillow — geometric distortion of the frame, when the lines bend inward and the picture becomes concave.
Fifty dollars, fifty dollars — a fixed lens with a focal length of 50 mm.
Polarik — polarizing light filter. Filters of this kind are a godsend for landscape photographers and effectively remove reflections from the surface of non-metallic objects (primarily from glass).
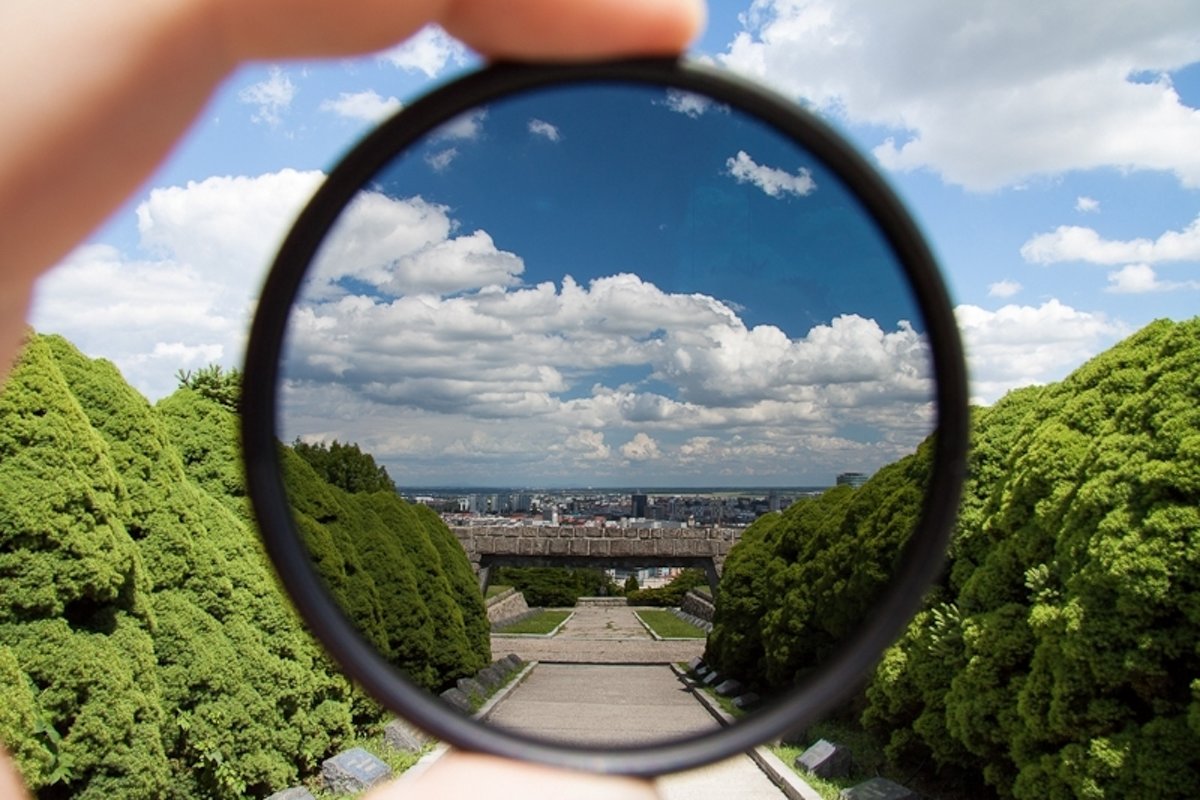 |
| A clear advantage of using a polarizing filter on a bright sunny day. |
A portrait lens is the common name for portrait lenses.
Mileage — the number of frames taken with the camera since the start of operation.
Failed shadows are dark areas of the image in which small details are indistinguishable.
Cannon (long-range cannon) — "folk" naming of ultrazooms and lenses with a large focal length, allowing you to shoot from a great distance to the target.
Dust shaker — built-in system for cleaning the matrix from dust.
A vacuum cleaner is a lens with a set of variable focal lengths, which noticeably changes in length when focus or focus, while drawing dust into the structure.
Puff — this is how the common people call a flash.
Pyatak, Piglet is an affectionate nickname for the Canon EOS 5D pro-series DSLRs).
RAW (RAW) — a "raw" photo recording format obtained straight from the matrix without processing. In the post-production stage of footage, RAW files open up the widest scope for creativity.
Retouching is the same as retouching. Those. process photographs.
Fisheye (fisheye) is an ultra wide-angle lens with characteristic bulging distortions at the edges of the frame. Distinctive features of fish-eye optics are short focal lengths (6-10 mm) and viewing angles of the order of 180 °C.
Boot is a joke name for Canon products.
The sensor is the same as the matrix.
Rate of fire — the maximum number of frames that the camera can "click" in 1 second.
Soft is a softening effect used in portrait photography.
A softbox is a flash attachment (usually a studio flash) used to scatter soft light.
A stub is an image stabilizer on board the lens or directly in the “carcass” of the camera, guarded against blurring at small camera movements and compensating for a couple of exposure steps when shooting handheld or in low light conditions. In addition, the stub ensures smooth images when recording video.
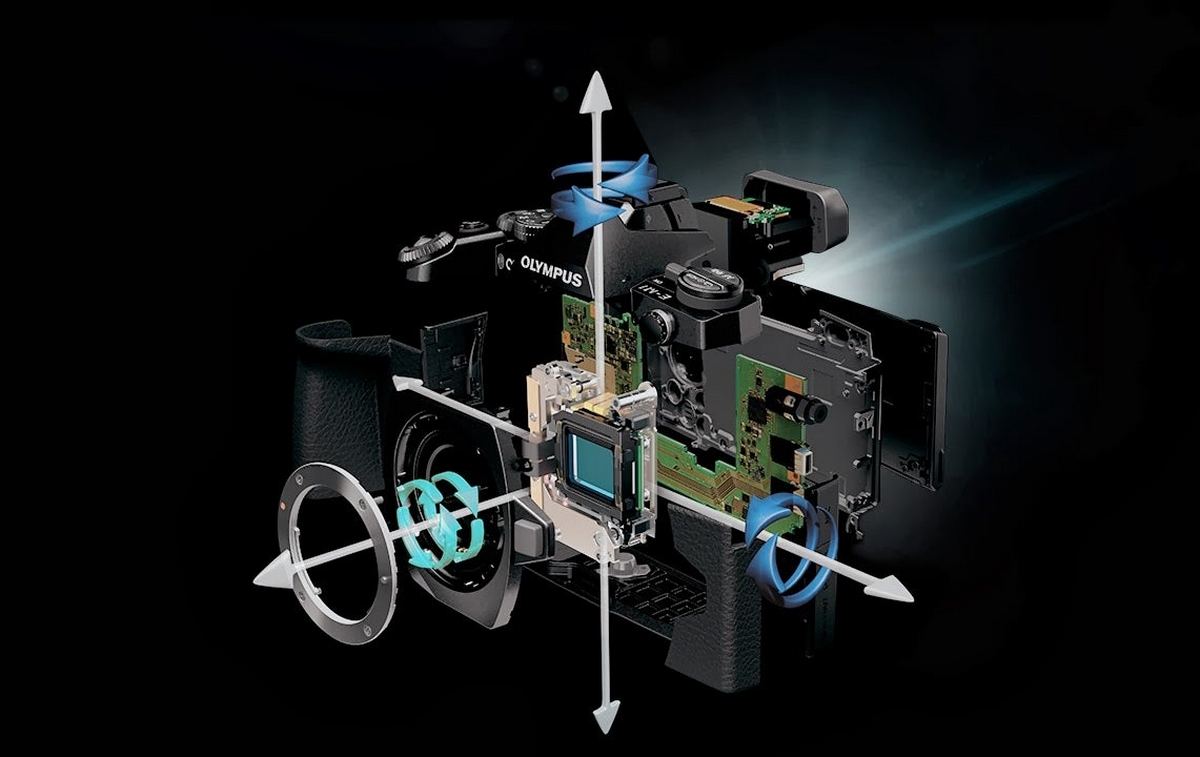 |
| In cameras with matrix stabilization systems, the image sensor is mounted on a movable stabilizing platform, which, with its movements, compensates for camera displacements along several axes. |
Glass is another option for naming a lens.
Stop — exposure level. The stop is equal to a twofold change in the amount of light falling on the matrix.
Telephoto — a long-focus lens (for "photo hunting" at long-range distances).
Warm — so they say when the optics produces an image of a reddish tint (for example, "My lens is warm").
Zoom — a mechanism for smoothly changing the focal length, synonymous with the term "zoom".
A tripod (tripod) is a tripod with three "legs". Usually foldable.
Carcass, body — a camera without a lens.
Fix — a lens with a constant (fixed) focal length.
Front focus — a miss of the automatic focus system due to incorrect autofocus algorithms, during which the camera constantly focuses in front of the object. It is found exclusively in SLR cameras.
Full frame (FF) is a camera with a full frame sensor.
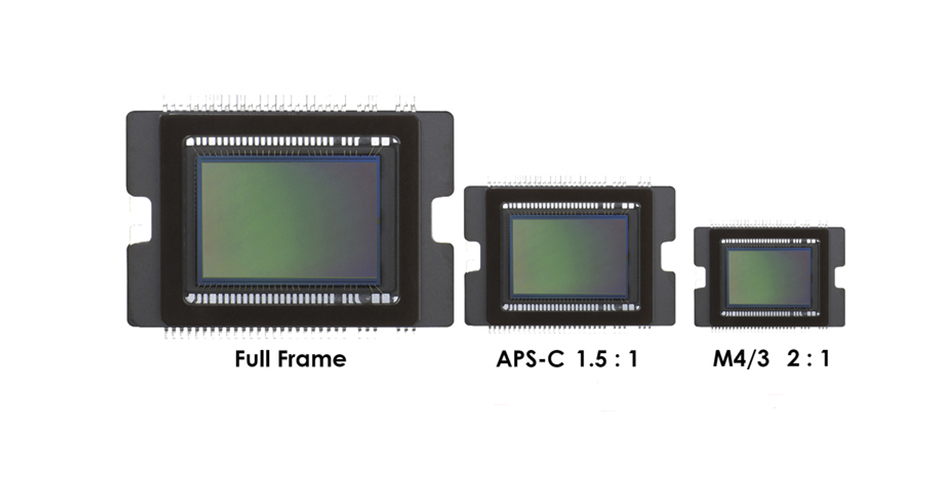 |
| Differences in the physical dimensions of common types of image sensors. |
HA — chromatic aberration. Those. colour distortions at the borders of high-contrast transitions from dark to light areas and vice versa.
The tail is the place where the lens is attached to the "body" of the camera.
The trunk is part of the design of the lens, the front lens of which noticeably moves forward when focus or zooming.
Shake — image blur due to unwanted camera shake at the time of shooting.
Shiri k — optics with a wide viewing angle.
A staff member is a universal lens for a permanent "registration" on the "carcass" of the camera (depending on the tasks of the photographer).
Noise reduction — processing algorithms for eliminating noise that occurs when shooting at high ISO.
Elka, Elechka are slang names for L-series lenses with outstanding optical characteristics for Canon cameras.
Good luck filming!
Articles, reviews, useful tips
All materials























































































